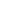
A company may, on a petition under section 272, be wound up by the ,—
(a) if the has, by special resolution, resolved that the company be wound up by the Tribunal;
(b) if the company has acted against the interests of the sovereignty and integrity of India, the security of the State, friendly relations with foreign States, public order, decency or morality;
(c) if on an application made by the or any other person authorised by the Central Government by under this Act, the Tribunal is of the opinion that the affairs of the company have been conducted in a fraudulent manner or the company was formed for fraudulent and unlawful purpose or the persons concerned in the formation or management of its affairs have been guilty of fraud, misfeasance or misconduct in connection therewith and that it is proper that the company be wound up;
(d) if the company has made a default in filing with the Registrar its or annual returns for immediately preceding five consecutive ; or
(e) if the Tribunal is of the opinion that it is just and equitable that the company should be wound up.
(1) A company may, on a petition under section 272, be wound up by the Tribunal,—
(a) if the company is unable to pay its debts;
(b) if the company has, by special resolution, resolved that the company be wound up by the Tribunal;
(c) if the company has acted against the interests of the sovereignty and integrity of India, the security of the State, friendly relations with foreign States, public order, decency or morality;
(d) if the Tribunal has ordered the winding up of the company under Chapter XIX;
(e) if on an application made by the Registrar or any other person authorised by the Central Government by notification under this Act, the Tribunal is of the opinion that the affairs of the company have been conducted in a fraudulent manner or the company was formed for fraudulent and unlawful purpose or the persons concerned in the formation or management of its affairs have been guilty of fraud, misfeasance or misconduct in connection therewith and that it is proper that the company be wound up;
(f) if the company has made a default in filing with the Registrar its financial statements or annual returns for immediately preceding five consecutive financial years; or
(g) if the Tribunal is of the opinion that it is just and equitable that the company should be wound up.
(2) A company shall be deemed to be unable to pay its debts,—
(a) if a creditor, by assignment or otherwise, to whom the company is indebted for an amount exceeding one lakh rupees then due, has served on the company, by causing it to be delivered at its registered office, by registered post or otherwise, a demand requiring the company to pay the amount so due and the company has failed to pay the sum within twenty-one days after the receipt of such demand or to provide adequate security or re-structure or compound the debt to the reasonable satisfaction of the creditor;
(b) if any execution or other process issued on a decree or order of any court or tribunal in favour of a creditor of the company is returned unsatisfied in whole or in part; or
(c) if it is proved to the satisfaction of the Tribunal that the company is unable to pay its debts, and, in determining whether a company is unable to pay its debts, the Tribunal shall take into account the contingent and prospective liabilities of the company.
(i) a balance sheet as at the end of the financial year;
(ii) a profit and loss account, or in the case of a company carrying on any activity not for profit, an income and expenditure account for the financial year;
(iii) cash flow statement for the financial year;
(iv) a statement of changes in equity, if applicable; and
(v) any explanatory note annexed to, or forming part of, any document referred to in sub-clause (i) to sub-clause (iv):
Provided that the financial statement, with respect to one person company, small company, dormant company and private company (if such private company is a start-up)may not include the cash flow statement;
Explanation. – For the purposes of this Act, the term ‘start-up’ or “start-up company” means a private company incorporated under the Companies Act, 2013 (18 of 2013) or the Companies Act, 1956 (1 of 1956) and recognised as start-up in accordance with the notification issued by the Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion, Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
Provided that on an application made by a company or body corporate, which is a holding company or a subsidiary or associate company of a company incorporated outside India and is required to follow a different financial year for consolidation of its accounts outside India, the Tribunal may, if it is satisfied, allow any period as its financial year, whether or not that period is a year:
Provided further that a company or body corporate, existing on the commencement of this Act, shall, within a period of two years from such commencement, align its financial year as per the provisions of this clause
Provided also that in case of a Specified IFSC public company, which is a subsidiary of a foreign company, the financial year of the subsidiary may be same as the financial year of its holding company and approval of the Tribunal shall not be required.
Provided also that in case of a Specified IFSC private company, which is a subsidiary of a foreign company, the financial year of the subsidiary may be same as the financial year of its holding company and approval of the Tribunal shall not be required.